August 14, 2025
How to Develop for the Next Generation of Smart Cities
How to Develop for the Next Generation of Smart Cities
Advanced technologies are quickly changing urban environments to improve efficiency, sustainability, and quality of life in smart cities. To automate traffic, waste disposal, and energy distribution, these cities use IoT devices, big data, AI, and 5G connection. Urban populations rise, requiring innovative solutions to tackle modern city issues. This article examines how developers may use IoT, data analytics, and AI to build creative smart city apps.
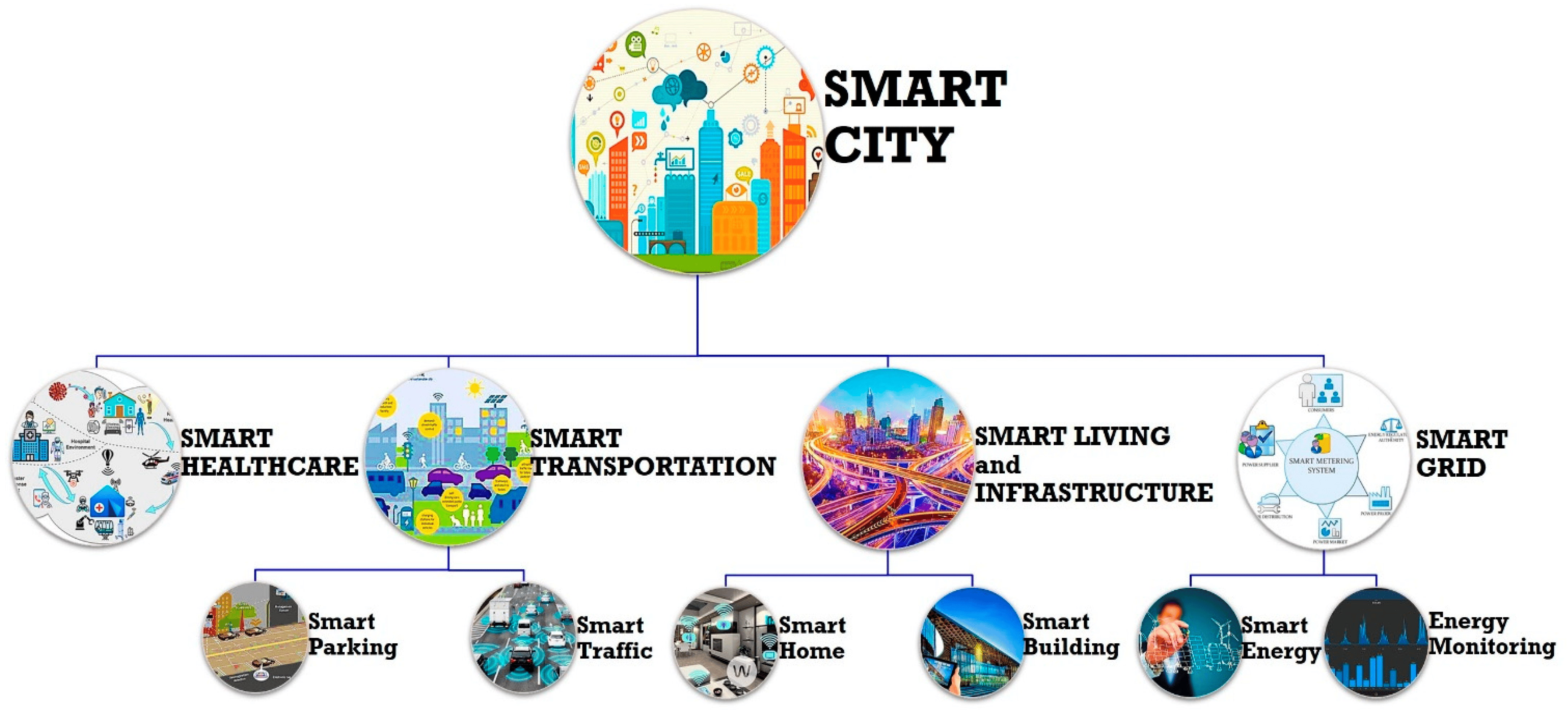
Understanding Smart City Core Technologies
Smart cities rely on numerous technologies to enhance urban life.
- IoT (Internet of Things): Sensors, smart meters, and cameras collect data for optimisation of city infrastructure. These gadgets measure traffic, trash, energy, and environmental concerns in real time.
- Big Data and AI: Analysing and interpreting large amounts of data requires analytics and AI. These technologies offer traffic, energy, and waste management predictive analytics.
- 5G connectivity: Enables real-time IoT device connectivity. 5G enables smart devices to communicate seamlessly with ultra-low latency and high data throughput.
- Cloud Computing: Smart cities use cloud computing for scalable data storage and processing, allowing efficient resource management.
Code Example: Simple IoT Sensor Data Collection in Python
import time
import random
class SmartCitySensor:
def __init__(self, sensor_id):
self.sensor_id = sensor_id
self.value = 0
def collect_data(self):
self.value = random.randint(0, 100)
return self.value
def main():
sensor = SmartCitySensor(sensor_id=1)
while True:
data = sensor.collect_data()
print(f"Sensor {sensor.sensor_id}: {data}")
time.sleep(1)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
Key Areas of Smart City Development
Smart cities increase services using innovative technology to solve urban issues. Key topics include:
- Smart Traffic Management: IoT sensors and cameras optimise traffic flow, decrease congestion, and avoid accidents. Smart lighting and adaptive traffic control systems improve journeys by adapting to traffic density.
- Smart Energy Solutions: IoT allows cities to optimise power grids by monitoring energy use. Energy efficiency using smart meters reduces expenses and environmental effect.
- Smart Waste Management: Sensors in trash bins notify authorities of fullness, optimising collection schedules and lowering garbage truck carbon footprint.
- Public Safety and Security: AI and surveillance cameras identify irregularities, enhancing safety and speeding up law enforcement response times.
Code Example: Smart Traffic Light System Adjustment
import random
class SmartTrafficLight:
def __init__(self, location):
self.location = location
self.state = "Red"
def adjust_light(self, traffic_density):
if traffic_density > 70:
self.state = "Green"
else:
self.state = "Red"
return self.state
def main():
traffic_density = random.randint(0, 100) # Simulating traffic density
light = SmartTrafficLight(location="Main Street")
new_state = light.adjust_light(traffic_density)
print(f"Traffic Light on {light.location} is now {new_state}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
Developing IoT Applications for Smart Cities
Smart cities use IoT devices to track traffic, air quality, energy use, and trash management. Developers must create apps that incorporate these devices with city's infrastructure.
- IoT Devices: Use sensors, cameras, and smart meters to gather real-time data.
- Data Processing: IoT devices create significant volumes of data that developers must effectively handle. Cloud platforms store and analyse this data.
- IoT Platforms: AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure IoT Hub provide deployment management and scaling.
Code Example: Sending IoT Sensor Data to AWS IoT
import boto3
import json
def send_data_to_aws(sensor_data):
client = boto3.client('iot-data', region_name='us-west-2')
payload = json.dumps({'sensor_data': sensor_data})
response = client.publish(
topic='smartcity/traffic',
qos=1,
payload=payload
)
print("Data sent to AWS IoT: ", response)
def main():
sensor_data = {"traffic_density": 80}
send_data_to_aws(sensor_data)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
Leveraging Big Data and AI for Smart Cities
Massive IoT data requires big data and AI to transform into useful insights.
- Big Data Analytics: Helps cities identify trends and optimise resource allocation by analysing data from IoT devices, social media, and public services.
- Machine Learning Models: These ML models can forecast traffic congestion, energy consumption, and optimise waste collection schedules.
- AI Decision-Making: Automate real-time decisions like traffic signal adjustments and energy distribution using AI algorithms.
Code Example: Predicting Traffic Density Using Machine Learning
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
import numpy as np
# Simulated traffic data (time, traffic_density)
data = np.array([[1, 40], [2, 45], [3, 50], [4, 55], [5, 60]])
X = data[:, 0].reshape(-1, 1) # Time
y = data[:, 1] # Traffic density
model = LinearRegression()
model.fit(X, y)
# Predict traffic density at time = 6
prediction = model.predict([[6]])
print(f"Predicted traffic density at time 6: {prediction[0]}")
Challenges in Developing Smart Cities
Smart city development faces many challenges regardless its benefits:
- Data Privacy and Security: Privacy and data security are problems with large-scale data collecting.
- Infrastructure Costs: Building and maintaining IoT infrastructure and cloud services for smart cities may be expensive.
- Interoperability: Ensuring seamless integration across systems, devices, and platforms is tough.
- Scalability: Meeting growing urban populations' expectations with smart city technology may be challenging and expensive.
Conclusion
Due to IoT, AI, big data, and cloud technologies, smart cities are the future of urban life. Developers provide new solutions that improve sustainability, efficiency, and quality of life. Smart solutions will become more necessary as cities develop, generating new developer possibilities.
585 views
